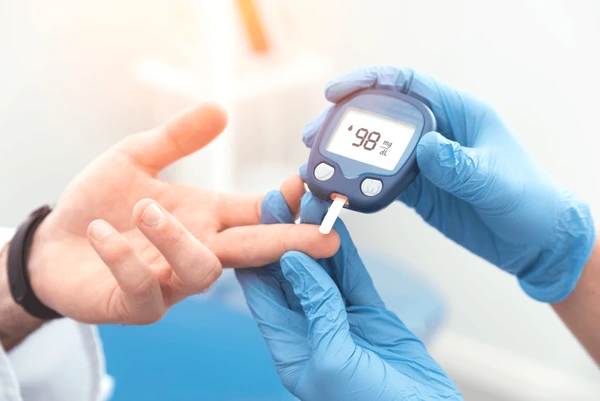
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing it. Fluctuations in blood sugar can lead to various complications, including cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, and kidney problems. Fortunately, several lifestyle modifications and dietary strategies can help keep blood sugar levels stable. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into various techniques and practices to manage metformin hcl 500 mg blood sugar effectively.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Before diving into strategies to manage blood sugar levels, it’s essential to understand what blood sugar is and how it affects the body. Blood sugar, or glucose, serves as the primary source of energy for cells. When we eat carbohydrates, the body breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate glucose levels by facilitating its uptake into cells for energy or storage.
However, problems arise when blood sugar levels become too high or too low. High blood sugar, known as hyperglycemia, can occur when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects. On the other hand, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can result from excessive insulin production, skipping meals, or overexertion.
Strategies to Keep Blood Sugar Levels Low
Healthy Eating Habits:
Follow a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Limit intake of sugary foods and beverages, refined carbohydrates, and processed snacks.
Monitor portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can lead to spikes in blood sugar.
Consider the glycemic index (GI) of foods, which measures how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Choose low-GI foods to help keep blood sugar stable.
Regular Physical Activity:
Engage in regular exercise, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, supplemented with strength training exercises.
Incorporate physical activity into daily routines, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or walking instead of driving for short distances.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
Check blood sugar levels regularly, especially for individuals with diabetes, using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system.
Keep a log of blood sugar readings to track patterns and identify factors that affect blood sugar levels.
Consult healthcare providers for guidance on target blood sugar ranges and adjustments to medication or insulin dosages.
Stress Management:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or tai chi to lower cortisol levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Prioritize self-care activities and allocate time for relaxation and leisure to reduce stress levels.
Adequate Sleep:
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support overall health and regulate hormone levels, including insulin.
Maintain a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day.
Create a conducive sleep environment by keeping the bedroom dark, quiet, and comfortable.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support kidney function, which plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels.
Limit consumption of sugary beverages and opt for water, herbal tea, or infused water instead.
Medication Adherence:
If prescribed medications or insulin to manage blood sugar levels, adhere to the recommended dosage and administration schedule.
Communicate regularly with healthcare providers to address any concerns or adjustments needed for medication management.
Regular Medical Check-ups:
Schedule regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor blood sugar levels, assess overall health, and detect any complications early.
Discuss preventive measures and lifestyle modifications to optimize blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and well-being, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing it. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including balanced eating, regular physical activity, stress management, adequate sleep, hydration, medication adherence, and regular medical check-ups, individuals can effectively keep blood sugar levels low and reduce the risk of complications. It’s crucial to personalize strategies based on individual needs and consult healthcare providers for personalized guidance and support in managing blood sugar effectively. With commitment and consistency, maintaining stable blood sugar levels is achievable, leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life. Read More…